How Long Do White Dwarfs Last
White dwarfs: Facts about the dumbo stellar remnants

White dwarfs are what is left when stars like our sunday accept exhausted all of their fuel. They are dense, dim, stellar corpses — the last observable stage of evolution for low- and medium-mass stars.
Whilst most massive stars will eventually go supernova, a low or medium mass star with a mass less than about viii times the mass of the sunday volition eventually get a white dwarf, according to NASA (opens in new tab). Approximately 97% of the stars in the Milky Fashion will eventually become white dwarfs, according to researchers (opens in new tab).
Compared to our sunday (opens in new tab), a white dwarf has a similar carbon and oxygen mass though it is much smaller in size — similar to Earth (opens in new tab), according to New Mexico Country University (opens in new tab) (NMSU).
White dwarf temperatures can exceed 100,000 Kelvin (opens in new tab) according to NASA (that's about 179,500 degrees Fahrenheit). Despite these sweltering temperatures, white dwarfs have a low luminosity as they're so small in size according to NMSU.
Related: Red dwarfs: The most common and longest-lived stars (opens in new tab)
White dwarf formation
Main-sequence stars (opens in new tab), including the lord's day, course from clouds of dust and gas drawn together past gravity. How the stars evolve through their lifetime depends on their mass. The nigh massive stars, with eight times the mass of the sun or more, will never become white dwarfs. Instead, at the end of their lives, white dwarfs will explode in a violent supernova (opens in new tab), leaving behind a neutron star (opens in new tab) or blackness hole (opens in new tab).
Did you know?
According to NASA, a teaspoon of white dwarf matter would weigh 5.5 tons on Earth — about the same as an elephant!
Smaller stars, however, will take a slightly more sedate path. Low- to medium-mass stars, such as the sun (opens in new tab), will eventually keen upward into cherry-red giants. After that, the stars shed their outer layers into a ring known as a planetary nebula (opens in new tab) (early observers thought the nebulas resembled planets such as Neptune (opens in new tab) and Uranus (opens in new tab) ). The core that is left behind will be a white dwarf, a husk of a star in which no hydrogen fusion occurs.

(opens in new tab)
Smaller stars, such as red dwarfs, don't make it to the red giant state. They simply burn through all of their hydrogen, catastrophe the process as a dim white dwarf. Nonetheless, red dwarfs take trillions of years to swallow their fuel, far longer than the xiii.eight-billion-year-former historic period of the universe, so no crimson dwarfs have all the same become white dwarfs.
White dwarf characteristics
When a star runs out of fuel, it no longer experiences an outward button from the process of fusion and information technology collapses in on itself. White dwarfs contain approximately the mass of the sun but accept roughly the radius of Earth, co-ordinate to Creation (opens in new tab), the astronomy encyclopedia from Swinburne University in Australia. This makes them amid the densest objects in infinite, beaten out just by neutron stars and blackness holes. According to NASA, the gravity on the surface of a white dwarf is 350,000 times that of gravity on Earth. That means a 150-pound (68-kilogram) person on World would weigh 50 one thousand thousand pounds (22.7 million kg) on the surface of a white dwarf.
(opens in new tab)
White dwarfs reach this incredible density because they are collapsed then tightly that their electrons are smashed together, forming what is called "degenerate matter." The former stars will keep collapsing until the electrons themselves provide enough of an outward-pressing forcefulness to halt the crunch. The more mass, the greater the pull inward, and so a more massive white dwarf has a smaller radius than its less massive counterpart. Those conditions hateful that, after shedding much of its mass during the red giant phase, no white dwarf tin exceed i.4 times the mass of the sun (opens in new tab).
When a star swells upwards to become a red behemothic, it engulfs its closest planets. But some can still survive. NASA's Spitzer spacecraft (opens in new tab) revealed that at least 1 to 3 percent of white dwarf stars have contaminated atmospheres that suggest rocky material has fallen into them.
"In the quest for World-similar planets, nosotros have now identified numerous systems which are excellent candidates to harbor them," Jay Farihi, a white dwarf researcher at the Academy of Leicester in England, told Space.com (opens in new tab). "Where they persist as white dwarfs, any terrestrial planets will not be habitable, but may take been sites where life adult during a previous epoch."
In one exciting case, researchers have observed the rocky material as it falls into the white dwarf.
"Information technology'due south heady and unexpected that we tin see this kind of dramatic change on human timescales," Boris Gänsicke, an astronomer at the University of Warwick in England, told Infinite.com (opens in new tab).
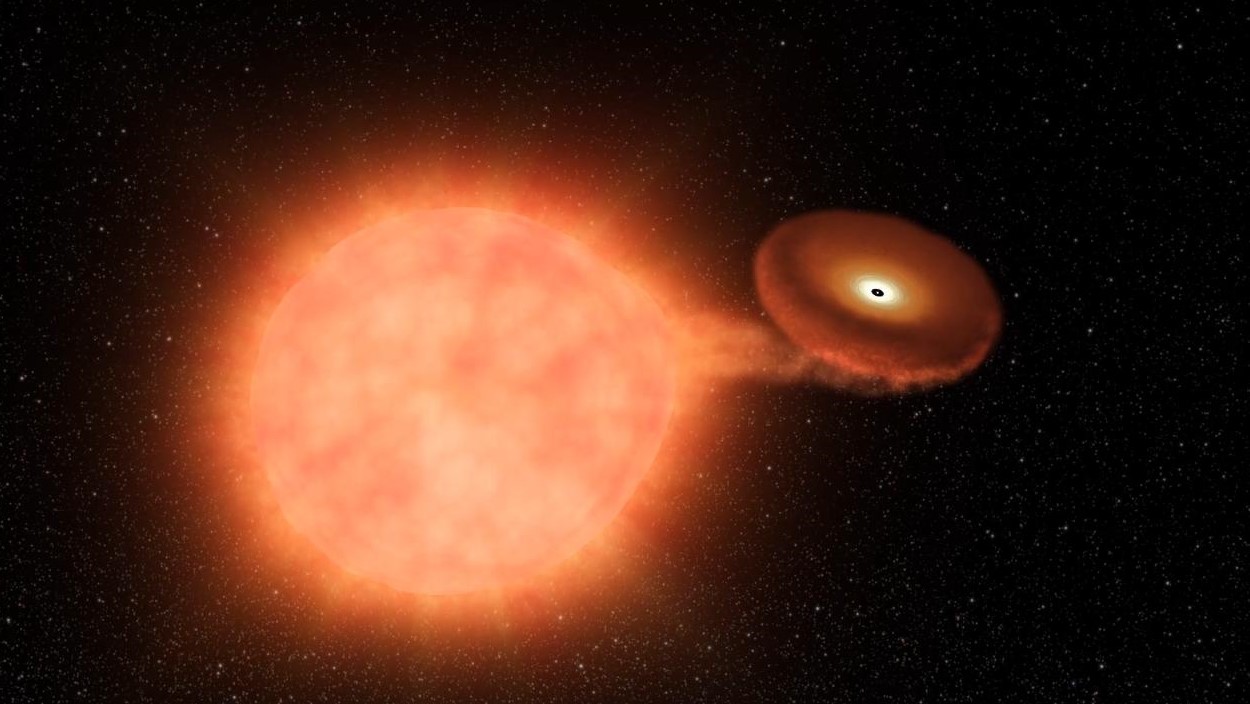
The fate of a white dwarf

(opens in new tab)
Many white dwarfs fade abroad into relative obscurity, eventually radiating away all of their energy and becoming so-called black dwarfs (opens in new tab), just those that share a system with companion stars may endure a different fate.
If the white dwarf is role of a binary system, it may be able to pull material from its companion onto its surface. Increasing the white dwarf'southward mass tin can have some interesting results.
One possibility is that the added mass could cause it to collapse into a much denser neutron star.
A far more explosive result is the Type 1a supernova (opens in new tab). As the white dwarf pulls textile from a companion star, the temperature increases, eventually triggering a delinquent reaction that detonates in a violent supernova that destroys the white dwarf. This procedure is known as a "single-degenerate model" of a Type 1a supernova.
Related: Know Your Novas: Star Explosions Explained (Infographic) (opens in new tab)
In 2012, researchers were able to closely observe the complex shells of gas surrounding one Type 1a supernova in fine particular.
"We actually saw, for the commencement time, detailed evidence of the progenitor for a Type 1a supernova," Benjamin Dilday, the study'southward lead author and an astronomer at Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network in California told Space.com (opens in new tab).
If the companion is some other white dwarf instead of an active star, the two stellar corpses merge together (opens in new tab) to boot off the fireworks. This process is known equally a "double-degenerate model" of a Type 1a supernova.
At other times, the white dwarf may pull just enough material from its companion to briefly ignite in a nova, a far smaller explosion. Because the white dwarf remains intact, it can repeat the process several times when information technology reaches that critical bespeak, breathing life back into the dying star over and again.
"These are the brightest and near frequent stellar eruptions in the galaxy, and they're often visible to the naked eye," Przemek Mróz, an astronomer at Poland'due south Warsaw University, told Space.com in a previous article.
Additional resources
Y'all can learn more about white dwarfs with ESA (opens in new tab) and explore different types of stars with NASA (opens in new tab). Discover the evolution of binary star systems with this free educational material from Lumen Learning (opens in new tab). Explore the physics of the universe with white dwarfs in this informative material from The University of Texas at Austin (opens in new tab).
Bibliography
- Dilday, B., et al. "PTF 11kx: A blazon Ia supernova with a symbiotic nova progenitor. (opens in new tab)" Science 337.6097 (2012): 942-945.
- Fontaine, Thou., P. Brassard, and P. Bergeron. "The Potential of White Dwarf Cosmochronology1. (opens in new tab)" Publications of the Astronomical Social club of the Pacific 113.782 (2001): 409.
- Horowitz, C. J. "Nuclear and night matter heating in massive white dwarf stars. (opens in new tab)" Physical Review D 102.eight (2020): 083031.
- Bédard, A., et al. "On the spectral development of hot white dwarf stars. I. A detailed model atmosphere assay of hot white dwarfs from SDSS DR12. (opens in new tab)" The Astrophysical Journal 901.ii (2020): 93.
- ESA "Shedding low-cal on white dwarfs — the future of stars like our sunday. (opens in new tab)" 2019
Join our Infinite Forums to go along talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if y'all have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Source: https://www.space.com/23756-white-dwarf-stars.html
Posted by: mullencrinver.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Long Do White Dwarfs Last"
Post a Comment